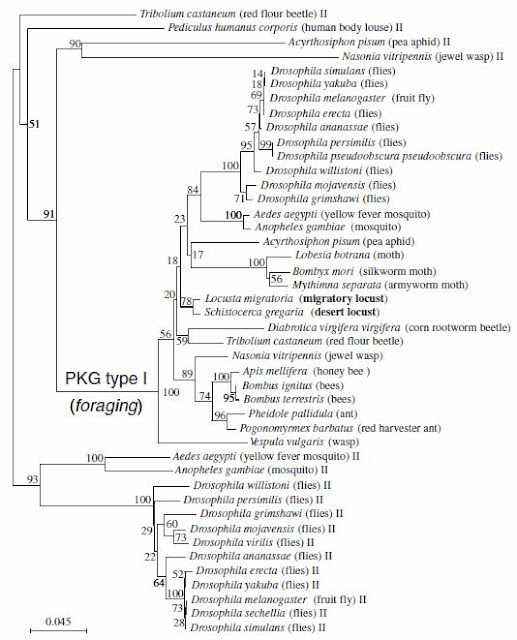
After my supervisor has seen the images from my second set of experiments, both of us went into a deep puzzle. He suggested that both of us should look deeper into literature that involved locust immunohistochemistry. One day, he sent me a paper that he thought I should ready and hopefully it help me to get the antibodies into the ganglia. Initially I was very skeptical at this paper because I didn't understand why would my supervisor send me a paper on locusts moulting rather than a paper on locusts' molecular biology or genetics which might actually involve immunostaining.
The paper he sent me involves studying the frontal ganglion (FP) and hormones involved during moulting. The background for this paper is that unlike vertebrates, invertebrate growth requires molting. Successful moultings are essential for insect survival, which requires highly regulated hormonal and behavior coordination.
Past studies have indicated that at least four hormones, pre-ecdysis triggering hormone (PETH), ecdysis triggering hormone (ETH), eclosion hormone (EH) and crustacean cardioactive peptide (CCAP), are involved in the process of two phases of moulting, pre-ecdysis and ecdysis.
During pre-ecdysis, motor patterns are believed to loosen the old and new cuticles. However, the insect does not extricate itself from its old cuticle until ecdysis. The pre-ecdysis behaviours were triggered by the effects of PETH and ETH acting on the central nervous system (CNS). Centrally released EH is thought then triggers ecdysis behaviour, either directly or followed by a release of CCAP within the CNS in a cGMP-dependent manner. CCAP then triggers the motor activities necessary to complete ecdysial behaviour.
The researchers in this paper have previously described a novel central pattern generator (CPG) network situated in the locust FG, and the motor patterns it generates. In the desert locust, Schistocerca gregaria, FG neurones innervate foregut dilator muscles and play a critical role in the control of foregut motor patterns in
different physiological and behavioural states. The researchers have presented the FG as an important target for chemical modulation.

During moulting, the foregut and FG are involved in air-swallowing behaviour. By filling the gut with air, the larval locust can generate enough internal pressure on the body wall to eventually split open the old cuticle, and to then stretch and shape the new adult cuticle and wings after the old cuticle has been shed at ecdysis. Frontal ganglionectomy abolishes air-swallowing and results in difficulty or failure in eclosion and wing expansion. A role for the FG during moulting has been reported for a number of insect species.
In this study, the researchers used suction electrodes to examine the FG CPG as an unexplored target for ecdysis peptides. They also examined the density of CCAP using immunoblotting, and the location of CCAP and cGMP through immunohistochemistry. In their study, they identified ETH, and PETH as FG bursting frequency promoters, while EH as a FG bursting frequency inhibitor.
 |
| Figure A illustrated that ETH significantly increased the burst frequency in locusts in CPG. Figure B illustrated both ETH and PETH can increase locusts' burst frequencies, however, ETH was a significantly potent burst frequency promotor than PETH. Figure C illustrated that after the application of EH, locusts' burst frequency stops, but the inhibition is not permanent. |
In addition, the researchers also identified CCAP as a potent modulator of the locust FG motor patterns. With applications of CCAP, frontal connectives (FC) and medial pharyngeal nerve (MPN) showed a significant increase in bursting frequency. The increased bursting frequency diminishes when CCAP is washed away with saline. In semi-intact preparations, CCAP also resulted in air bubbles in the crop, which is presumably the effect of air swallowing. Their results imply a novel role for this peptide in generating air swallowing behaviour during the early stages of ecdysis.
 |
| Figure A demonstrated that after CCAP application, there is a significant increase in burst frequency within the FC and MPN. However, the effects of CCAP can be diminished after washing the tissue. Figure B illustrated the air bubbles formed on top of the tissue after CCAP application as the result of air swallowing. |
Last but not the less, from immunostaining researchers found that one to three CCAP-immunoreactive neurones in the tritocerebrum that extended through the FC nerve and gave rise to extensive arborization within the neuropil of the FG. Their immunostaning examined the variation in the number of CCAP immunoreactive axons in the FG neuropil at the different stages. In mid-larvae only one to two (mostly one) fibres were stained, whereas at the air-swallowing stage at least three afferent fibres were visible. As ecdysis progressed the number of stained axons then declined. A quantitative analysis concluded that the area of CCAP-immunoreactive neuropil increased during airswallowing and decreased at late ecdysis.
 |
| These series of immunostaining illustrates the number of CCAP-immunostaining reactive axons and the size of CCAP-immunostaining reactive neuropil in the the FG. These images demonstrated that the number of CCAP related axons increases in size as moulting occurs, but drops at late ecdysis, same logic applies to the size of CCAP related neuropil. |
After all findings on regulators on locusts moulting, the part of this paper that might really help me in my project is found in their immunostaining section, when they stated '... (the tissues) were incubated in 0.5 – 1.0 mg/ml collagenase in PBSTX for 30 – 60 min at room temperature to aid in antibody penetration.' This is exactly what I wanted to read! Since my problem was that my antibodies wasn't entering the cells. This definitely gave me new energy on returning to my experiments again.
However, the part I didn't like in this paper was that many of the factors in the immunostaining had a relative large uncertainty in their incubation time. For example, as mention earlier, the tissues were incubated between 30 to 60 mins in collagenase, which might caused a difference by itself in staining results. Furthermore, this would mean I had to try the difference time frames during different incubation processes too to find an optimal time myself.
Ref:
Zilberstein, Y., Ewer, J., Ayali, A., 2006. Neuromodulation of the locust frontal ganglion during the moult: a novel role for insect ecdysis peptides. The Journal of Experimental Biology. 209:2911-2919.